Radius of Curvature Model
Radius of Curvature Model
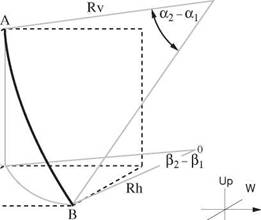
This model assumes a curved path which has the shape of a spherical arc passing through the measured angles at the two survey stations (Figure 6). Essentially, the inclination and direction are assumed to vary linearly over the course length. This method is less sensitive to errors, even if the survey interval is relatively long. The calculations however, are complicated and are best handled by computer.
|
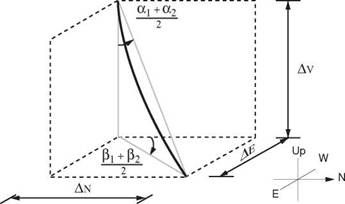
Figure 5 Average Angle Model |
|
|
|
0 |
|
E |
|
N |
|
E |
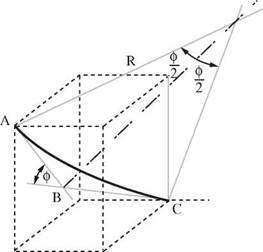
This model takes the space vectors defined by inclination and direction measurements and smooths these onto the wellbore curve (Figure 7). The curvature of the path is calculated using a ratio factor, defined by the dog-leg of the wellbore. The result of minimising the total curvature within the physical constraints of the wellbore is an arc. Again the calculations are best handled by computer.
|
Figure 7 Minimum Curvature Model |