POWER SYSTEM
POWER SYSTEM
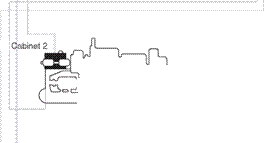
Most drilling rigs are required to operate in remote locations where a power supply is not available. They must therefore have a method of generating the electrical power which is used to operate the systems mentioned above. The electrical power generators are driven by diesel powered internal combustion engines (prime movers). Electricity is then supplied to electric motors connected to the drawworks, rotary table and mud pumps (Figure 2). The rig may have, depending on its size and capacity, up to 4 prime movers, delivering more than 3000 horsepower. Horsepower (hp) is an old, but still widely used, unit of power in the drilling industry.
|
net 1 |
|
f ‘—bo CLJ С (___________ Engine Generator 1 j |
|
|
|
Control Cabinet |
|
Mud Pump |
|
|
|
Control Cab |
|
Control |
|
Engine Generator Engine Generator 2 J |
|
Control Cabinet 3 |
|
Drillers Controller I |
|
|
|
Mud Pump |
|
|
|
(if required) |
|
|
|
aEs^ Rotary Table Draw Works |
Figure 2 Power system
Older rigs used steam power and mechanical transmission systems but modern drilling rigs use electric transmission since it enables the driller to apply power more smoothly, thereby avoiding shock and vibration. The drawworks and the mud pumps are the major users of power on the rig, although they are not generally working at the same time.