. Gasifier efficiency
. Gasifier efficiency
An important factor determining the actual technical operation, as well as the economic feasibility of using a gasifier system, is the gasification efficiency.
A useful definition of the gasification efficiency if the gas is used for engine applications is:
Н-ХО,
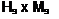 ^=тЛ-^х100
^=тЛ-^х100
In which: г) m = gasification efficiency (%) (mechanical)
Hg = heating value of the gas (kJ/m3), (see table 2.1 g or 2.3)
Qg = volume flow of gas (m3/s)
Hs = lower heating value of gasifier fuel (kJ/kg) (see section 2.6)
Ms = gasifier solid fuel consumption (kg/s)
If the gas is used for direct burning, the gasification efficiency is sometimes defined as:
(HgX^MQgXFfexC^xAT)
TLv = —11——————— ——- X 100
In which:
г) th = gasification efficiency (%) (thermal) p g = density of the gas (kg/m3)
Cp = specific heat of the gas (kJ/kg°K)
Д T = temperature difference between the gas at the burner inlet and the fuel entering the gasifier (°K).
Depending on type and design of the gasifier as well as on the characteristics of the fuel Am may vary between 60 and 75 per cent. In the case of thermal applications, the value of r) № can be as high as 93 percent
|
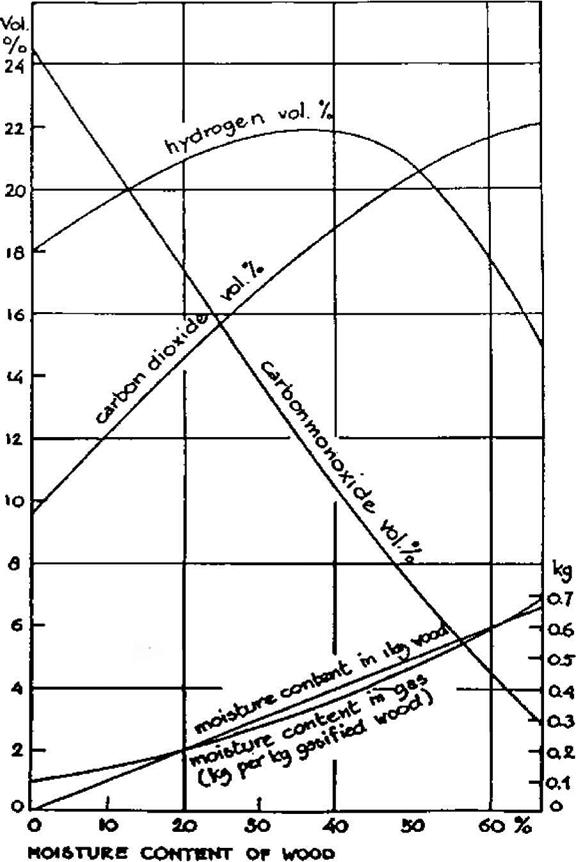
Figure 2.4 Woodgas composition as a function of wood moisture content (15%-heat loss)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|